The Y2K Panic Wave
As the clock ticked toward the year 2000, panic and parties collided in a cultural storm dubbed Y2K. While tech experts scrambled to prevent a digital meltdown, the world braced for everything from toasters revolting to planes crashing. Here are 20 wild truths behind the chaos.
 Keira McPhee from Van Rock City, Canada on Wikimedia
Keira McPhee from Van Rock City, Canada on Wikimedia
1. The Y2K Bug Was Decades In The Making
Programmers in the 1960s and 1970s often used two digits to represent years, saving memory. “99” made sense then, but “00” risked being misread as 1900. The oversight impacted banking systems, power grids, and government records globally by the late '90s.
 The Computer Bug That Almost Ended The World | The Y2k Debacle by NationSquid
The Computer Bug That Almost Ended The World | The Y2k Debacle by NationSquid
2. The U.S. Government Spent $100 Billion On Fixes
Preventing potential Y2K catastrophes didn’t come cheap. American companies and agencies spent over $100 billion updating software, testing systems, and reprogramming old code. The IRS spent about $1 billion ensuring tax systems wouldn’t crash on January 1, 2000.
 The Computer Bug That Almost Ended The World | The Y2k Debacle by NationSquid
The Computer Bug That Almost Ended The World | The Y2k Debacle by NationSquid
3. Some Believed The Apocalypse Was Coming
For survivalists and conspiracy theorists, Y2K meant end times. Panic buying led to stockpiles of fuel and food. One Kansas man built a concrete bunker equipped with a well and solar power in preparation for what he believed would be months of societal collapse.
 The Computer Bug That Almost Ended The World | The Y2k Debacle by NationSquid
The Computer Bug That Almost Ended The World | The Y2k Debacle by NationSquid
4. Russia's Nukes Were A Top Global Concern
World leaders worried that flawed Y2K code might accidentally launch missiles. Russia’s outdated nuclear systems were especially troubling. To prevent misfires, the U.S. and Russia jointly staffed a command center in Colorado Springs through the date rollover to monitor for accidental launches.
 User:Croquant with modifications by User:Hex on Wikimedia
User:Croquant with modifications by User:Hex on Wikimedia
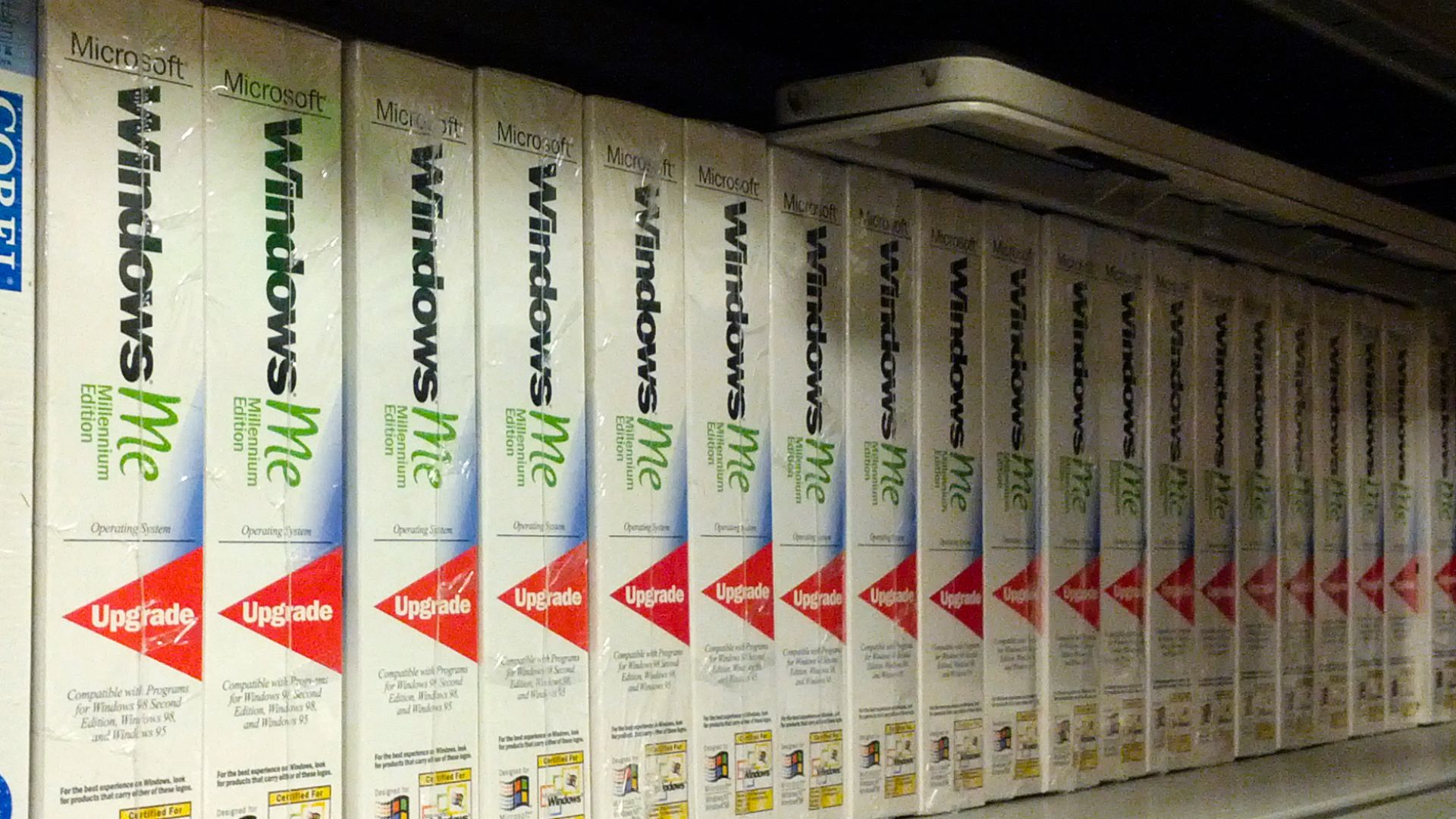
5. Big Brands Used Y2K In Ads
Marketing departments didn’t miss a beat. Microsoft promoted Windows Millennium Edition (ME), highlighting its ease of use and reassuring users that the computer would transition smoothly into the 2000s. Pepsi joined in, promising to deliver “the joy of the new millennium—without the bugs.”
6. Airlines Took Precautions But Kept Flying
Despite widespread fears, major airlines didn’t ground flights. Carriers like United and American Airlines ran pre-scheduled test flights before New Year’s Eve to reassure travelers. Ultimately, no aviation incidents were reported globally due to Y2K software glitches.
7. Some Countries Celebrated Early To Test The Waters
Island nations such as Kiribati were among the first to enter the year 2000. These nations allowed tech observers to watch for any disruption. However, when early time zones passed without issue, celebrations in other countries became far more relaxed.
8. ATMs Were Watched Like Hawks
Banking systems were prime suspects for failure. Banks tested their ATMs extensively, fearing machines might eat cards, miscalculate balances, or shut down. In New York City, thousands of technicians were on call that night—yet nearly all machines worked without a hitch.
9. The CIA Monitored Global Infrastructure
U.S. intelligence agencies went beyond watching for terrorism. They tracked international Y2K vulnerabilities, especially in power grids and communication systems. The CIA even briefed President Clinton daily on potential trouble spots, including oil pipelines in the Middle East and telecom systems in Asia.
10. Not All Glitches Were Harmless
Some Y2K bugs slipped through. In Japan, a nuclear power plant’s radiation monitoring system failed temporarily at midnight. In the U.S., 150 slot machines in Delaware malfunctioned. Although minor, these incidents proved the bug wasn’t entirely hype-driven: it wasn’t the digital apocalypse.
11. Canada Froze All Government Flights Temporarily
For several minutes after midnight, Canada grounded all federal aircraft, including Coast Guard and military planes. Once systems confirmed the correct date readings and operational status, flights resumed. The brief pause was part of a nationwide plan known as Operation Abacus.
 Tech. Sgt. Ezequiel Rodriguez on Wikimedia
Tech. Sgt. Ezequiel Rodriguez on Wikimedia
12. Wall Street Was On High Alert
Financial markets took no chances. The New York Stock Exchange hired hundreds of IT staff to test systems throughout 1999 and ran final checks on New Year’s Eve. When markets opened on January 3, 2000, trading ran smoothly without a single Y2K-related error.
 USA: NEW YORK STOCK EXCHANGE CONDUCT Y2K COMPUTER TESTS by AP Archive
USA: NEW YORK STOCK EXCHANGE CONDUCT Y2K COMPUTER TESTS by AP Archive
13. U.S. Prisons Reviewed Their Door Systems
Concerns emerged that automated prison doors might inadvertently open due to a faulty date code. Some facilities conducted manual overrides or temporarily disabled automatic systems during the date rollover. No documented incidents occurred, but the possibility added a strange twist to Y2K paranoia.
14. India Became A Y2K Tech Powerhouse
Indian IT firms played a massive role in the Y2K fix. Companies like Infosys took on contracts from U.S. and European clients. This surge in demand positioned India as a global tech leader and laid the groundwork for its 21st-century outsourcing boom.
 Ashwin Kumar from Bangalore, India on Wikimedia
Ashwin Kumar from Bangalore, India on Wikimedia
15. COBOL Programmers Came Out Of Retirement
The programming language COBOL—widely used in legacy systems—was key to the Y2K fix. As demand spiked, retired programmers were called back to work. Some earned six-figure contracts to update old code banks, mostly in the finance and government sectors.
16. A UN Task Force Tracked Global Readiness
The UN launched the International Y2K Cooperation Center to help coordinate worldwide preparedness. Led by Bruce McConnell, the task force monitored readiness in over 170 countries. It helped nations with fewer resources tackle critical systems like water, energy, and health services.
 USA: GLOBAL CONFERENCE ON YEAR 2000 COMPUTER BUG by AP Archive
USA: GLOBAL CONFERENCE ON YEAR 2000 COMPUTER BUG by AP Archive
17. Tech Companies Made A Fortune Off The Panic
Firms specializing in software updates saw huge profits. Companies like IBM and Oracle offered Y2K compliance solutions, while startups emerged solely to handle bug-proofing. Gartner Group estimated that globally, total Y2K spending exceeded $300 billion by the end of 2000.
18. Power Plants Ran Manual Controls Overnight
Utilities didn’t trust automation to handle the date change. In many countries, nuclear and coal plant operators switched to manual controls for several hours. For example, in the U.K., National Grid staff supervised control rooms continuously to ensure uninterrupted electricity distribution.
19. Italy Was One Of The Least Prepared Nations
Unlike the U.S. and the U.K., Italy lagged in Y2K readiness. A 1999 European Commission report ranked it near the bottom in government and banking sector preparedness. Still, the country experienced no major failures, largely because many Italian systems were still analog or minimally computerized.
20. January 1, 2000, Was One Of The Quietest Days Ever
Despite the noise leading up to it, the new millennium arrived with minimal disruption. No planes crashed, no satellites failed, and global infrastructure held strong. Also, U.S. emergency call centers reported fewer incidents than a typical New Year’s Day.
KEEP ON READING

The story of Ching Shih, the Woman Who Became the…
Unknown author on WikimediaFew figures in history are as feared…
By Emilie Richardson-Dupuis Dec 29, 2025
Einstein's Violin Just Sold At An Auction—And It Earned More…
A Visionary's Violin. Wanda von Debschitz-Kunowski on WikimediaWhen you hear…
By Ashley Bast Nov 3, 2025
This Infamous Ancient Greek Burned Down An Ancient Wonder Just…
History remembers kings and conquerors, but sometimes, it also remembers…
By David Davidovic Nov 12, 2025
The Mysterious "Sea People" Who Collapsed Civilization
3,200 years ago, Bronze Age civilization in the Mediterranean suddenly…
By Robbie Woods Mar 18, 2025
This Famous Historical Figure Died Broke And Unknown
Art Institute of Chicago on UnsplashHistory is full of names…
By Sara Springsteen Feb 14, 2026
20 Soldiers Who Defied Expectations
Changing the Rules of the Battlefield. You’ve probably heard plenty…
By Annie Byrd Feb 10, 2026