20 Historical Events That Changed the World More Than People Realize
Overlooked Moments That Shaped History
History books often highlight wars and leaders, but many pivotal events receive far less attention despite their profound influence on global society, technology, and politics. These moments quietly reshaped economies, cultures, and daily life in ways that continue to affect us today. The following 20 events demonstrate this dynamic, showing transformations that altered the course of human development more than commonly acknowledged.
 Cecil Stoughton, White House on Wikimedia
Cecil Stoughton, White House on Wikimedia
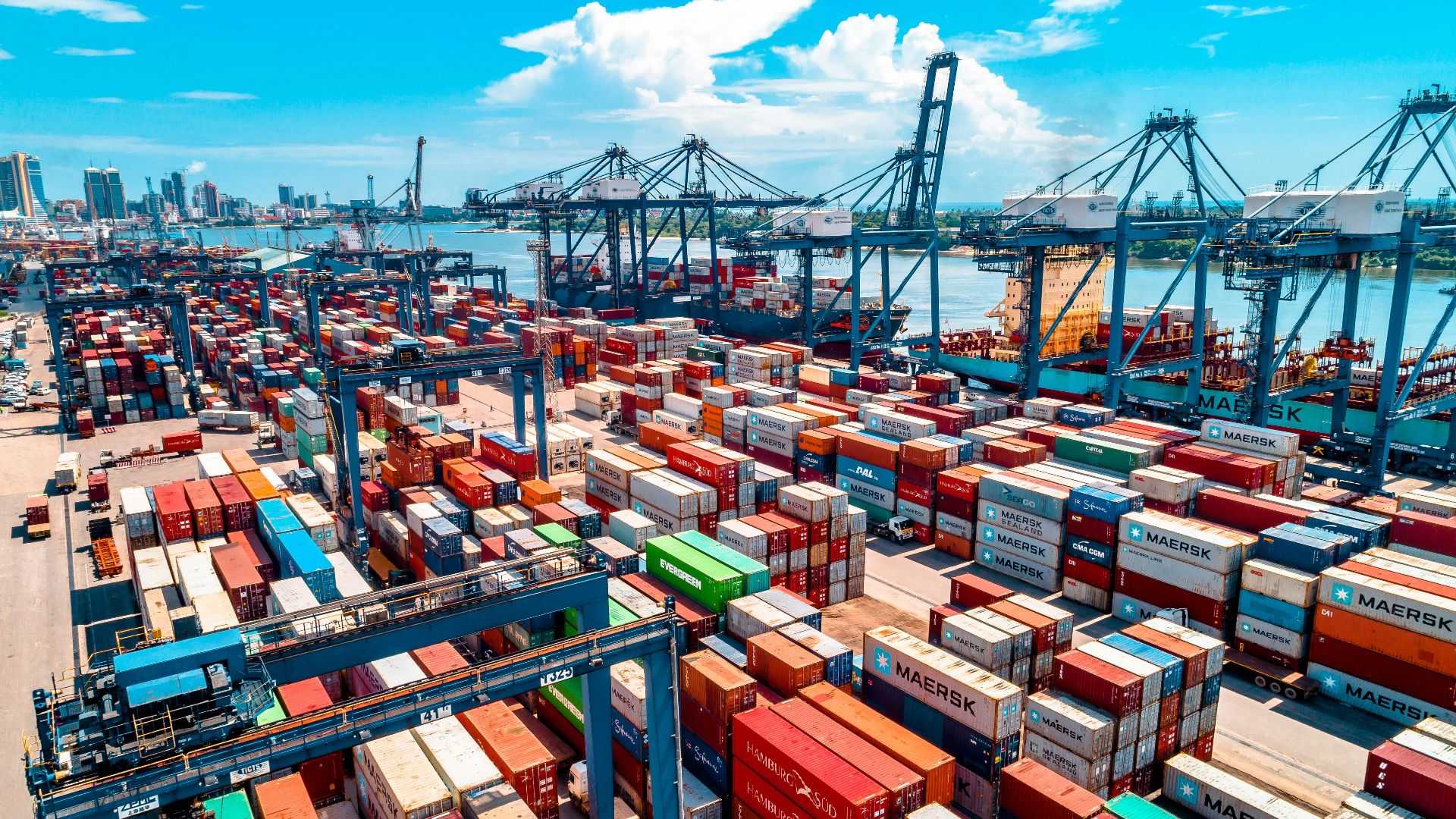
1. Invention Of The Shipping Container (1956)
Malcolm McLean introduced standardized steel shipping containers in 1956, revolutionizing global trade by making loading and unloading vastly more efficient. Before this innovation, cargo handling relied on manual labor and custom packing, causing endless delays, damage, and high costs at ports worldwide. The container system slashed shipping expenses by up to 90 percent, fueling globalization and modern supply chains.
2. Green Revolution (1960s-1970s)
Norman Borlaug's high-yield, disease-resistant wheat varieties sparked the Green Revolution, boosting food production in countries like Mexico, India, and Pakistan. This breakthrough averted famines threatening billions through better seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation techniques. It transformed global food security and supported population growth.
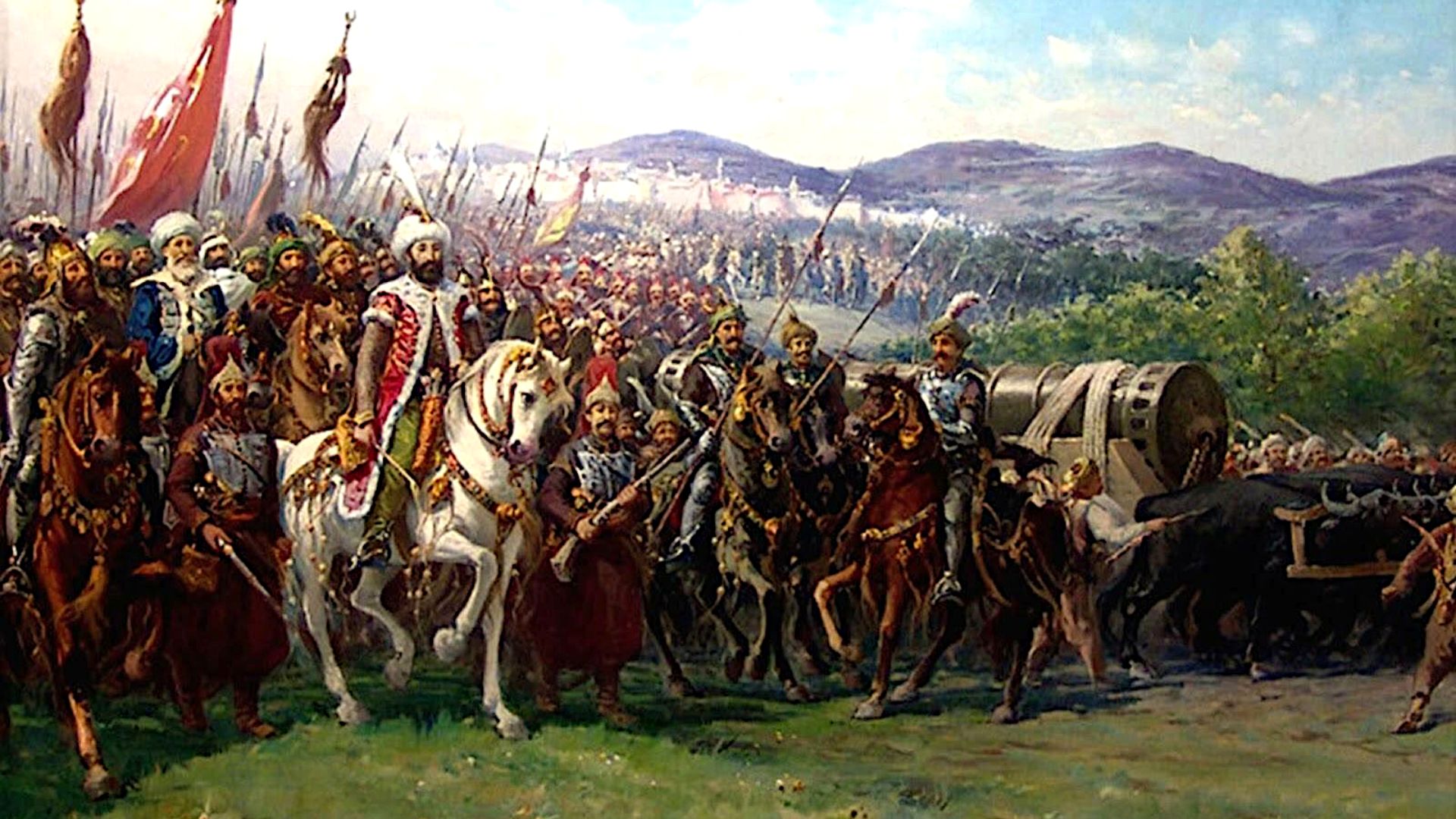
3. Fall Of Constantinople (1453)
Ottoman forces captured Constantinople in 1453, ending the Byzantine Empire and redirecting Silk Road trade to sea paths around Africa. European powers sought maritime alternatives for Asian goods, spurring the Age of Discovery. This shift moved economic power from the Mediterranean to the Atlantic, effectively changing the world.
4. Meiji Restoration (1868)
Japan's Meiji Restoration ended feudal isolation, adopting Western technologies and military reforms rapidly under Emperor Meiji. Japan industrialized in the decades, defeating Russia in 1905 and becoming Asia's first modern power. This challenged European dominance in the Pacific.
 Unknown authorUnknown author on Wikimedia
Unknown authorUnknown author on Wikimedia
5. Berlin Airlift (1948-1949)
Western Allies airlifted 2.3 million tons of supplies to West Berlin during the Soviet blockade, sustaining civilians without concession. This feat cemented Cold War divisions and NATO alliances and established U.S. containment strategies for decades.
 Unknown photographer on Wikimedia
Unknown photographer on Wikimedia
6. Stanislav Petrov's Decision (1983)
Soviet officer Stanislav Petrov disregarded a false missile alert on September 26, 1983, preventing nuclear escalation. His skepticism averted a counterstrike during Cold War tensions. This preserved global peace at a critical moment.
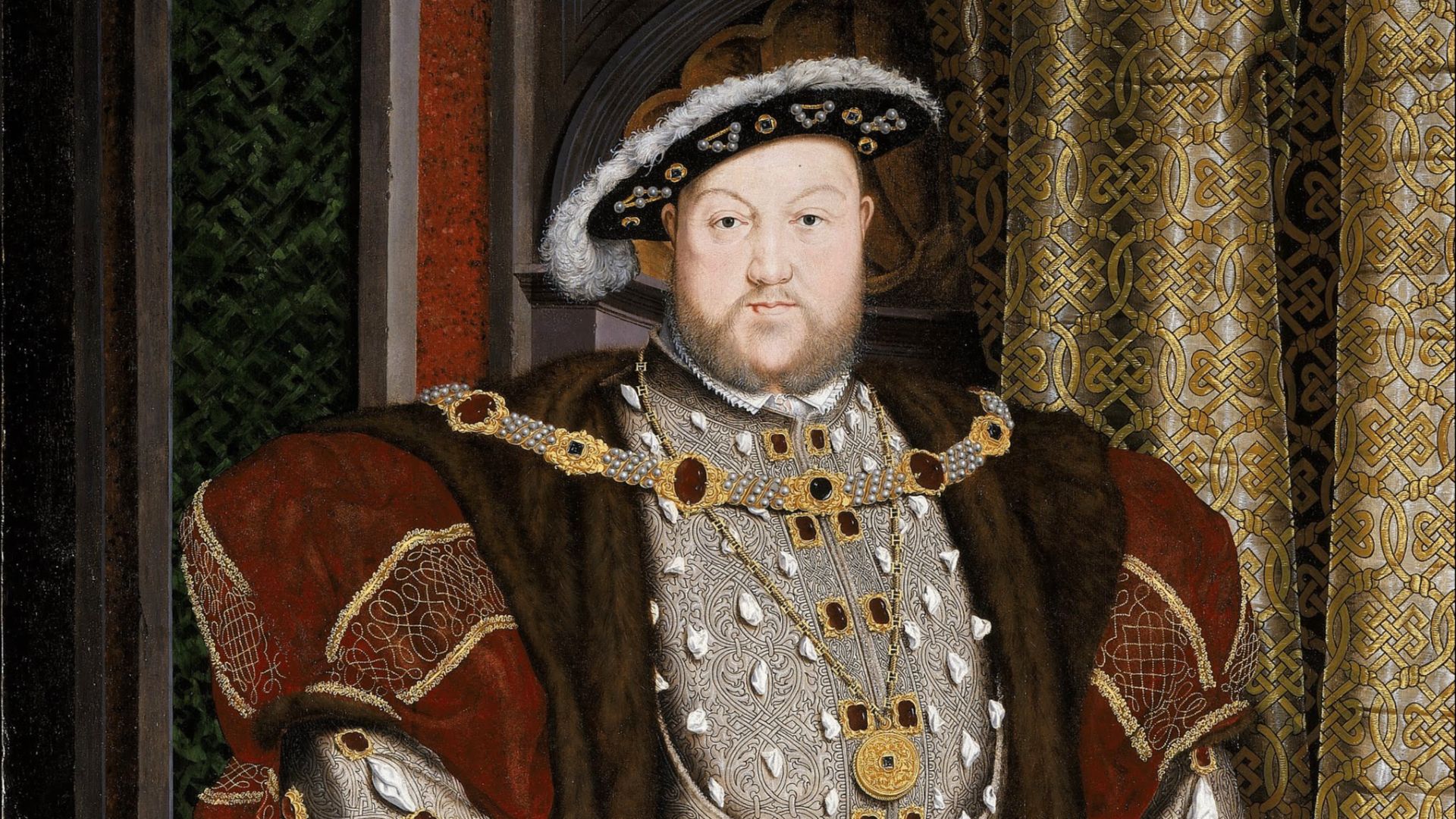
7. Dissolution Of The Monasteries (1536-1541)
King Henry VIII dissolved England's monasteries between 1536 and 1541, seizing vast lands and wealth to fund his government and redistribute to loyal nobles. This dismantled the Catholic Church's economic power in Britain, accelerating the English Reformation. Furthermore, land reforms created a new gentry class that shaped politics for centuries.
 After Hans Holbein the Younger on Wikimedia
After Hans Holbein the Younger on Wikimedia
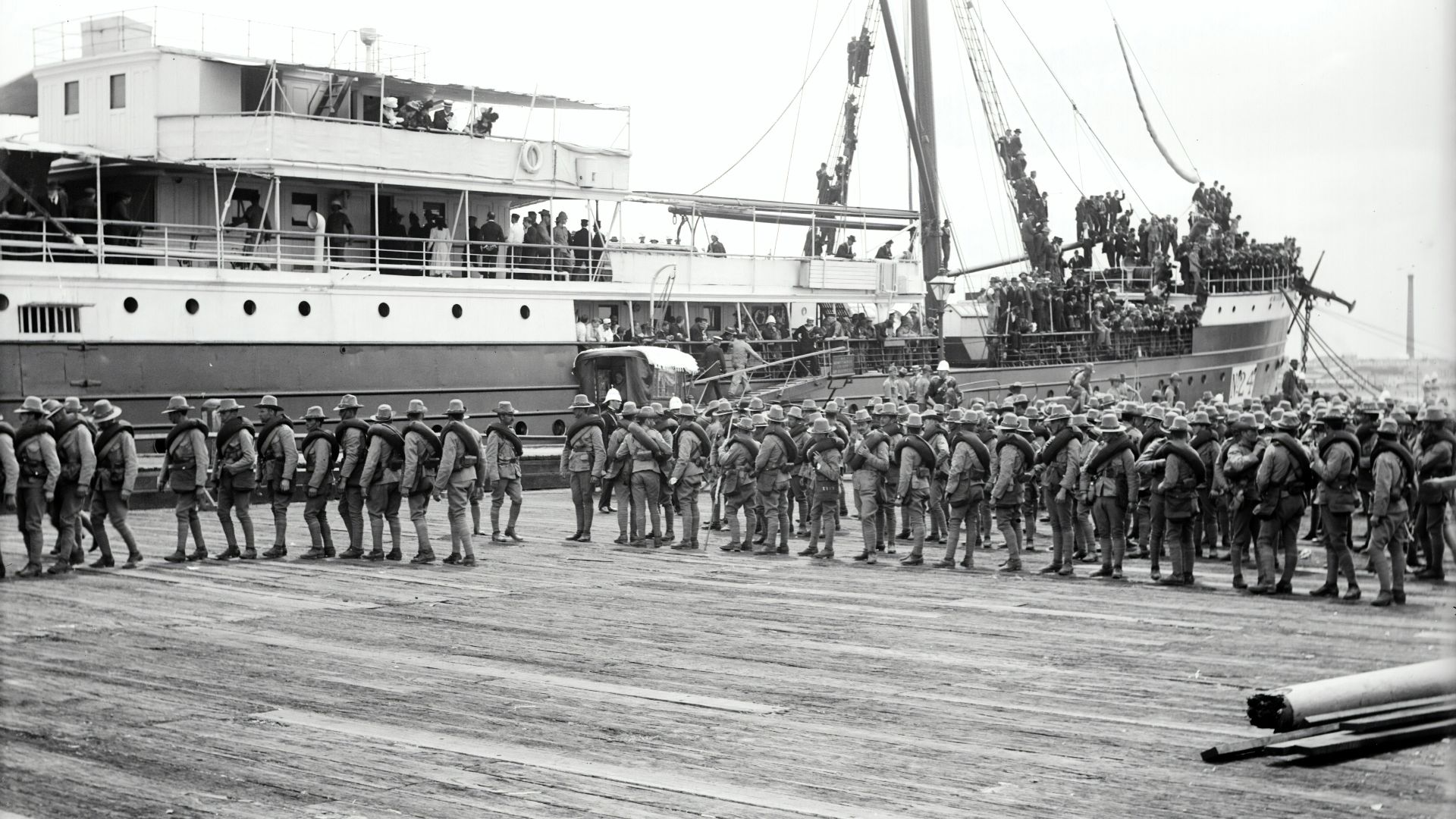
8. Zimmermann Telegram (1917)
British codebreakers intercepted Germany's 1917 telegram proposing a Mexico alliance against the U.S., drawing America into World War I. U.S. resources secured Allied victory and elevated American global power. The event ended isolationism and shifted Europe's geopolitical landscape.
9. Mount Tambora Eruption (1815)
Mount Tambora's 1815 eruption caused "The Year Without a Summer" with global cooling, crop failures, and famines. It prompted food innovations and cultural works like Frankenstein. This highlighted volcanic climate impacts early on.
 Ása Steinarsdóttir on Unsplash
Ása Steinarsdóttir on Unsplash
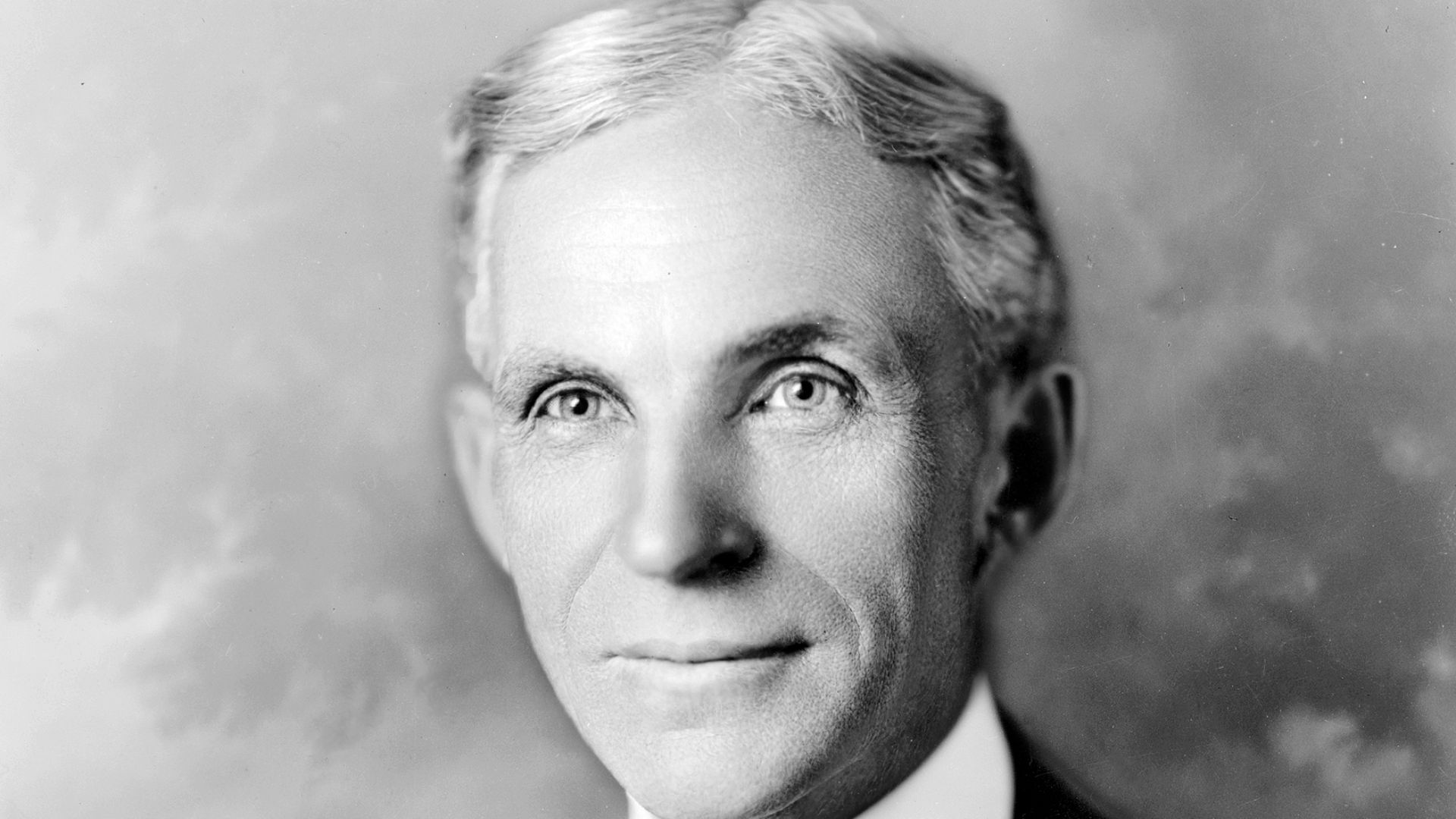
10. Henry Ford's Assembly Line (1913)
Henry Ford's 1913 moving assembly line slashed Model T production to 93 minutes, making cars affordable for the masses. Mass production spread globally, sparking motorization and consumer culture. It redefined manufacturing and labor.
11. Oneida Corn Relief At Valley Forge (1778)
The Oneida Nation delivered corn to Washington's starving troops at Valley Forge in 1778, preventing total military collapse. This aid enabled training and Revolutionary victories, and helped sshapeNative alliances.
12. Vasili Arkhipov's Veto (1962)
Soviet officer Vasili Arkhipov vetoed a nuclear torpedo launch during the Cuban Missile Crisis. His restraint de-escalated the superpower standoff nd avoided an atomic war that would have had catastrophic results.
13. Compromise Of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 balanced slavery tensions by recognizing California as a free territory. It delayed the Civil War but deepened divisions. However, these political realignments intensified and created a ripple effect.
14. Battle Of Jumonville Glen (1754)
George Washington's 1754 ambush sparked the French and Indian War, expanding to the Seven Years' War. It bankrupted Britain, prompting colonial taxes and revolution. As a result, empires were forced to realign.
 unknown illustrator on Wikimedia
unknown illustrator on Wikimedia
15. Partition Of India (1947)
Britain's 1947 partition displaced 15 million, causing massive violence and South Asian rivalries. Radcliffe's border created wars and nuclear tensions, as regional geopolitics shifted dramatically. The event continues influencing migration patterns today.
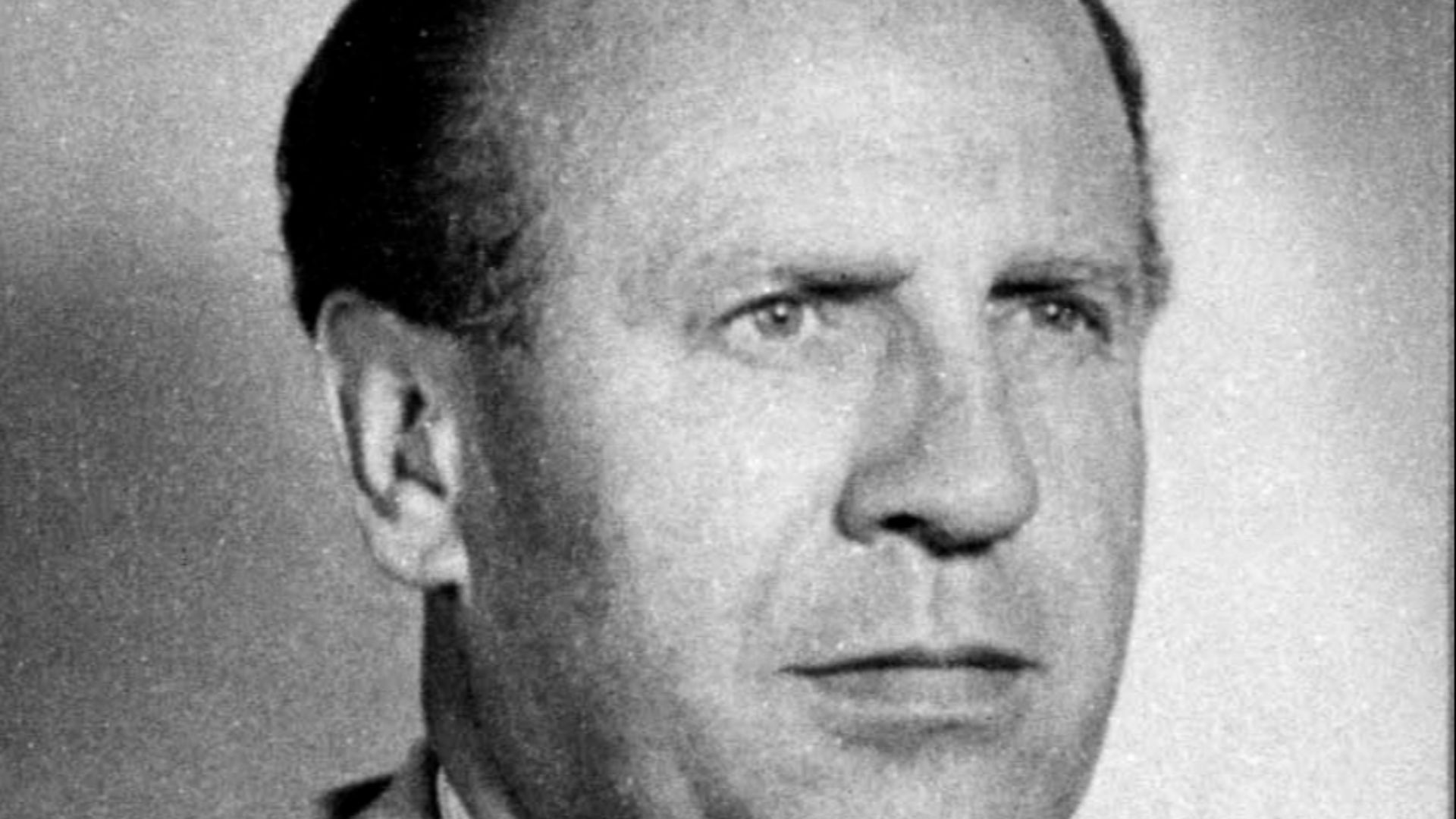
16. Oskar Schindler's Courage (1943-1945)
Oskar Schindler saved 1,200 Jews via factory employment amid Holocaust risks. His defiance exemplified resistance against genocide. It influenced Holocaust remembrance worldwide, and survivors' descendants preserve his legacy actively to this day.
 Unknown authorUnknown author on Wikimedia
Unknown authorUnknown author on Wikimedia
17. Norman Conquest (1066)
William the Conqueror's victory at the Battle of Hastings in 1066 established Norman rule over England, replacing Athe Anglo-Saxonaristocracy with French-speaking elites. This brought feudal land tenure and centralized royal administration that strengthened the monarchy's power across the realm. The Domesday Book survey of 1086 created Britain's first comprehensive land registry, influencing taxation and governance for centuries.
18. Black Death (1347-1351)
This plague killed 30-60 percent of Europe, shattering feudalism through labor shortages. It accelerated urbanization and Renaissance thought. Modern labor economics emerged from these shifts, and wage systems replaced serf obligations permanently.
19. Great Schism Of 1054
In 1054, mutual excommunications between Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholic churches formalized Christianity's east-west divide after centuries of tension. This split reshaped religious authority, art, philosophy, and power structures across Europe. Theological differences hardened into separate civilizations.
20. Beaver Wars (17th Century)
Iroquois fur trade wars controlled Great Lakes commerce, stalling French growth. These conflicts reshaped alliances and trade patterns. Colonial expansion adapted to Native power dynamics, and trade routes defined early American economies.
KEEP ON READING

20 Greek Gods We Don't Often Talk About
Step Aside, Zeus. Greek mythology isn’t only about Zeus and…
By Elizabeth Graham Jan 16, 2026
10 Historic Courtship Practices That Should Be Brought Back &…
Old-School Dating Was a Mix of Charming & Unhinged. Historic…
By Emilie Richardson-Dupuis Jan 20, 2026
Legendary Tales: 20 Most Fascinating Mythical Creatures from Folklore
Mythological Beasts. Stories about mythical creatures endure for a simple…
By Christy Chan Jan 16, 2026
10 Successful British Kings & 10 That Failed Spectacularly
What Does “Successful” Really Mean?. Success can mean different things…
By Elizabeth Graham Jan 21, 2026
The 20 Craziest Silent Films Ever Made
When Silence Let the Madness Speak. Silent cinema didn’t just…
By Chase Wexler Jan 5, 2026
10 Things Gladiator Got Right About Ancient Rome & 10…
Between Historical Truth and Cinematic Illusion. Ridley Scott’s Gladiator won 5 Academy…
By Chase Wexler Jan 17, 2026














