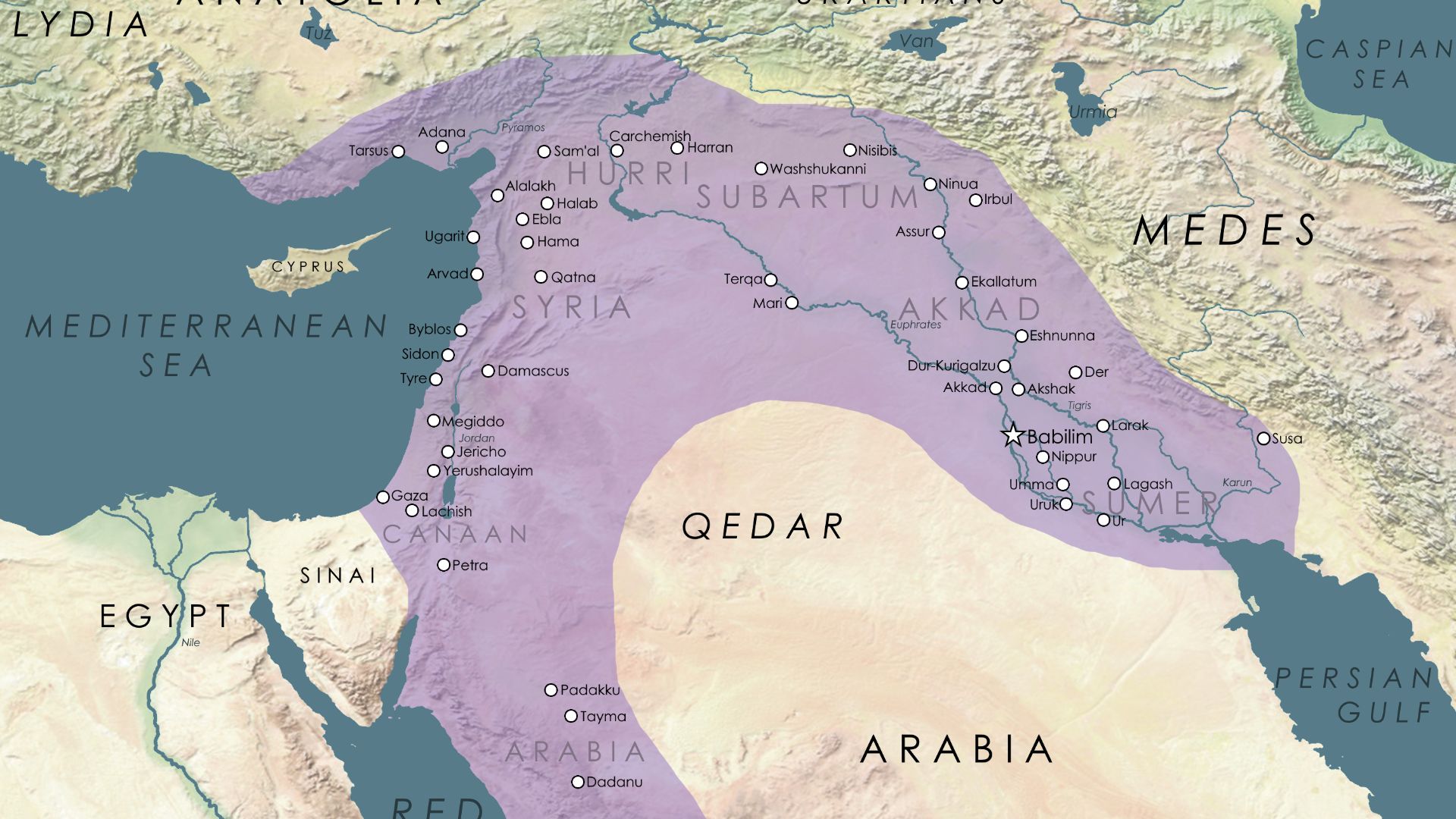
The Fertile Crescent: 20 Ancient Civilizations That Started Society As We Know It
Thank You For Your Service
Human society had to start somewhere, and thanks to advances in archeology, anthropology, history, and sociology, we know that human society started in several somewheres. We have these ancient civilizations to thank for the building blocks of the world we live in today, as well as many foundational tools, systems, and laws we all take part in.
1. Ancient Mesopotamia
Ancient Mesopotamia is one of the earliest known sites of human development, with artifacts dating back to 10,000 BCE. Mesopotamia is cited as being the birthplace of the wheel, cereal crops, cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture. Ancient Mesopotamia covers parts of modern-day Iraq, Iran, Turkey, Syria, and Kuwait.
 Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg) on Wikimedia
Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg) on Wikimedia
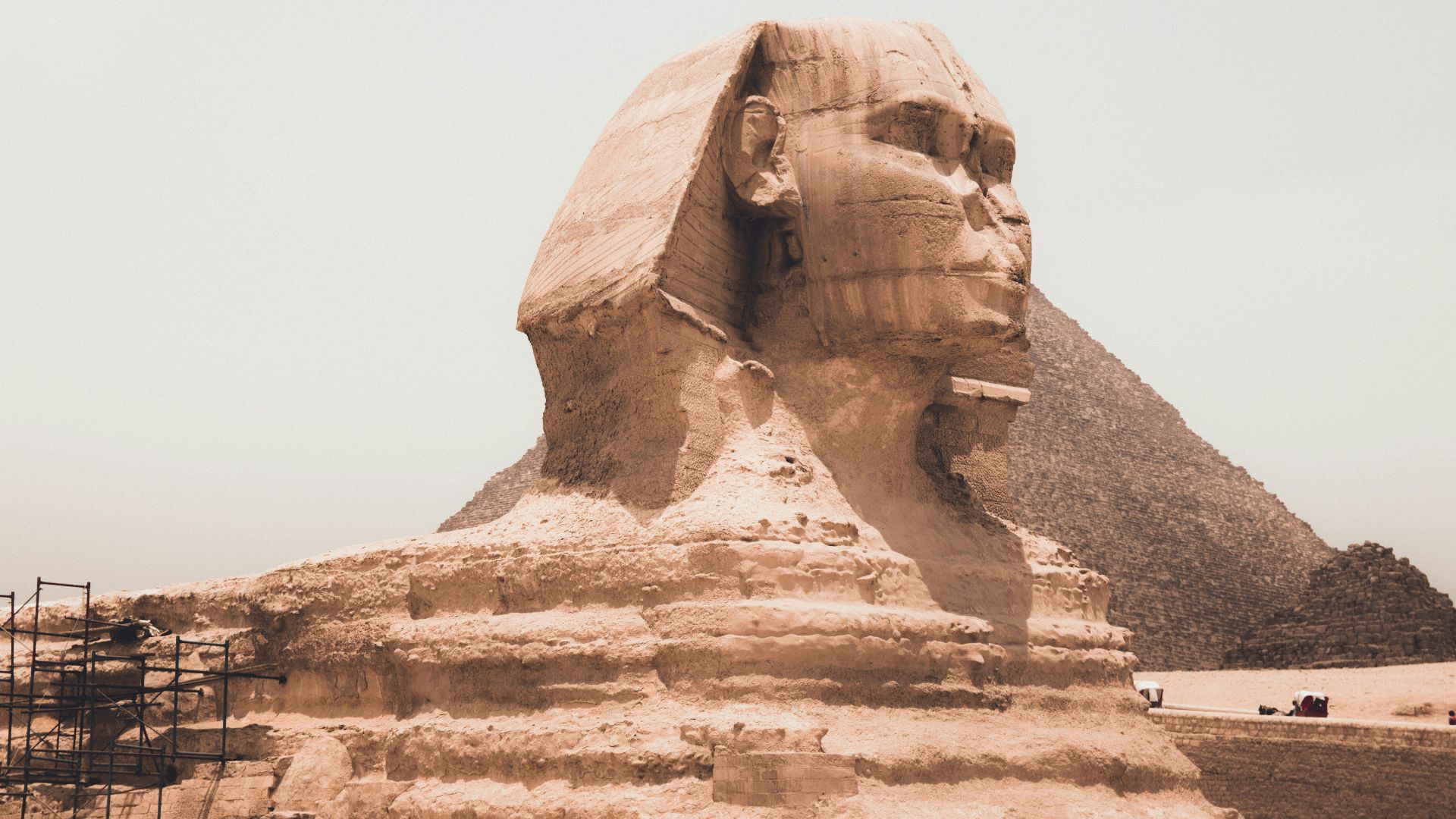
2. Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt’s history is thousands upon thousands of years old, and its prehistoric period was longer than the time between its first dynasty and today. The actual Predynastic Egypt period existed from 6210 BCE to 3000 BCE, and is responsible for the creation of pottery, organized religion, and organized political systems.
 Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China on Wikimedia
Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China on Wikimedia
3. Indus Valley Civilization
This particular civilization lasted from 3300 to 1300 BCE and was located in parts of modern-day Pakistan, India, and Afghanistan. The Indus Valley Civilization is well-known for creating incredible feats of urban planning, drainage systems, and shipbuilding, on top of creating the first-known standardized measuring system.
4. Ancient China
Similar to Egypt, China has existed for millennia, and has a rich and complex history that’s kept historians interested in it for centuries. Ancient China is known for the “Four Great Inventions”: the compass, gunpowder, papermaking, and printing.
5. Minoan Civilization
This Bronze-Age society existed on the island of Crete and on the Aegean Sea. It lasted from 3100 to 1100 BCE, and began constructing complex urban settlements around 2000 BCE. The Minoans are known for creating the first flushing toilet, the potter’s wheel, and multi-story buildings.
6. Norte Chico Civilization
Located in modern-day Peru, the Norte Chico (or Caral-Supe) Civilization thrived from the fourth to the second millennia BCE. It’s considered the oldest-known civilization in America. This civilization is best known for its impressive architecture and landscaping techniques.
 Luz Maria Linarez Huacausi on Wikimedia
Luz Maria Linarez Huacausi on Wikimedia
7. The Olmecs
One of the two cradles of civilizations in the Americas, the Olmecs existed in modern-day Mexico from 1200 to 400 BCE. The Olmecs were some of the first to practice ritual bloodletting, the Mesoamerican ballgame, and the creation of very large pieces of artwork, such as the colossal heads.
8. Mycenaean Civilization
This particular civilization is considered the last phase of ancient Greece’s Bronze Age. Existing from 1750 to 1050 BCE, it is the first time this geographical area saw urban organization, writing systems, palatial states, and artwork. They’re also responsible for innovations in the engineering, architecture, and military fields.
9. Ancient Rome
While maybe not the founding fathers of civilization, Ancient Rome is well-known for its strong military, extensive road systems, aqueducts, law systems, architecture, governance, and language. Ancient Rome technically existed from the 8th to the 5th century BCE, when the western empire fell.
 Unknown authorUnknown author on Wikimedia
Unknown authorUnknown author on Wikimedia
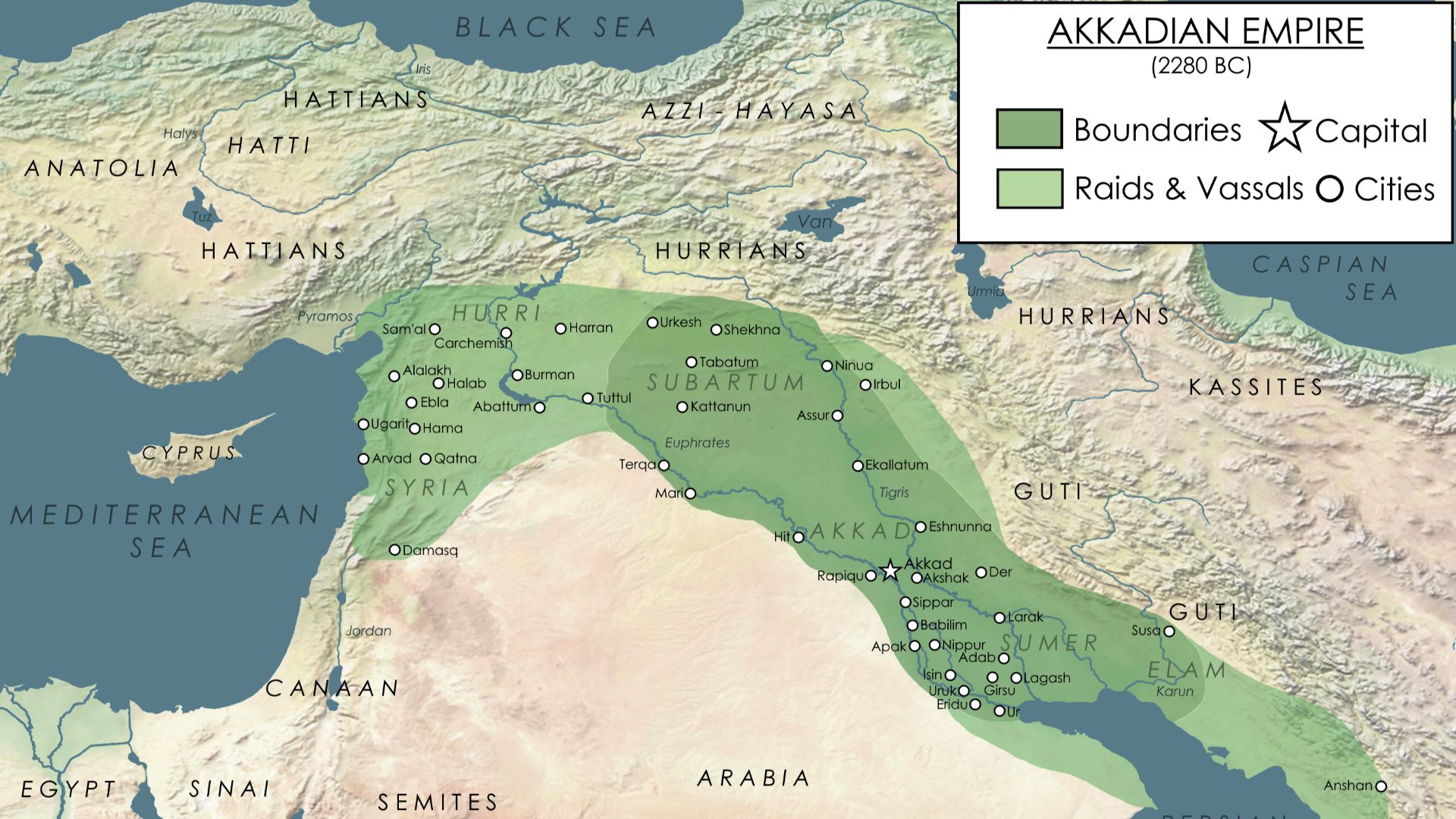
10. Akkadian Empire
Considered the first known empire, the Akkadian Empire influenced other Mesopotamian cultures from 2334 to 2154 BCE. While a part of the larger feats ancient Mesopotamia achieved, the Akkadians made a name for themselves as they made developments in art, technology, and long-distance trade.
11. Inca Empire
The Inca Empire was the largest in the Americas before colonization, and existed from 1438 to 1572. While they had no writing system or knowledge of iron or steel, it’s noted that the Incas still created incredible stonework art, a road network, textiles, record keeping by knotted strings, and agricultural innovations.
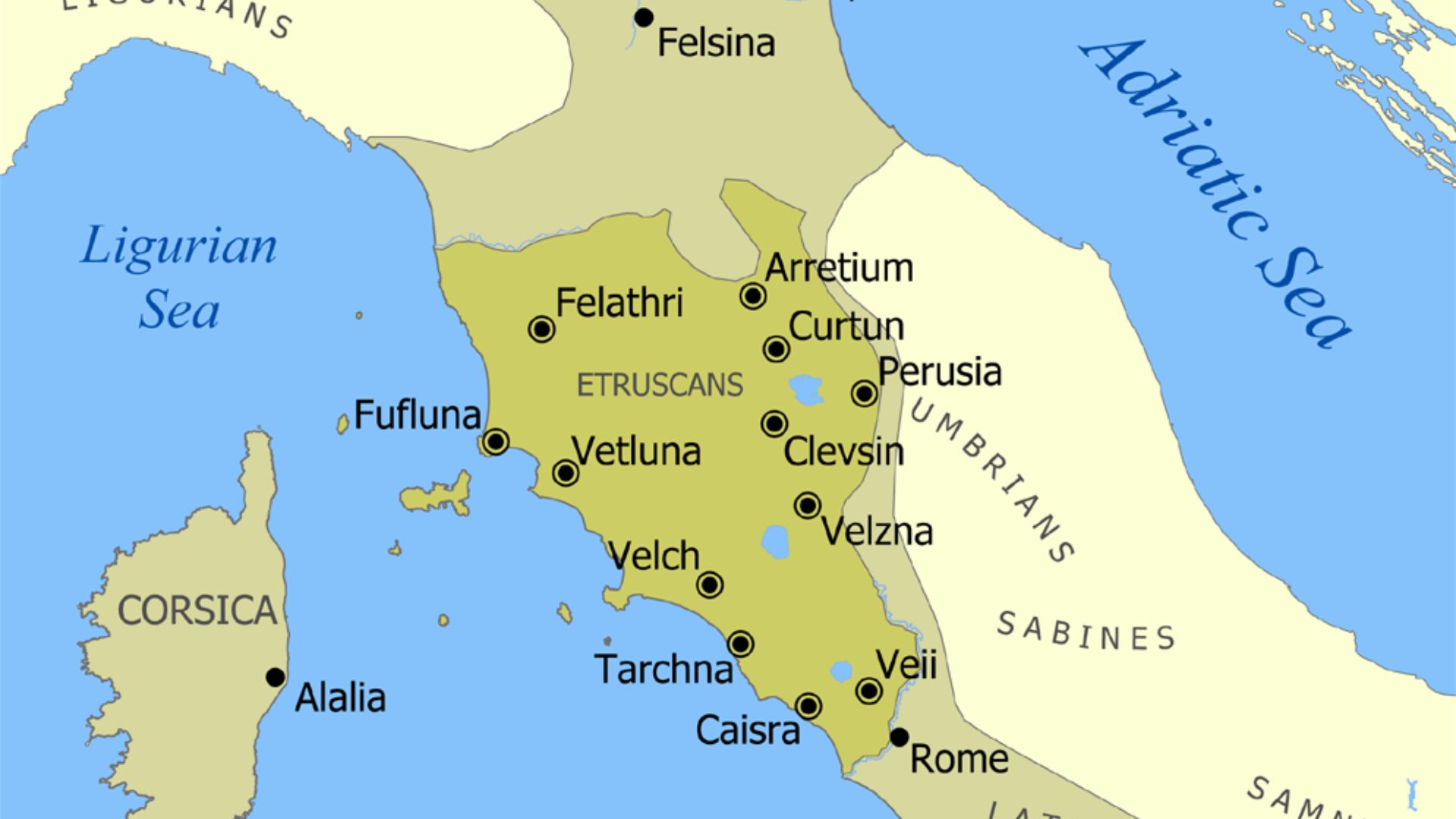
12. Etruscan Civilization
Existing in the north-western side of modern-day Italy, the Etruscans evolved from Villanovan culture, an Iron Age culture of Italy. The Etruscans are best known for vibrant art, advanced metalworking, gold jewelry, and funerary frescoes.
13. Xia Dynasty
The Xia Dynasty was the first dynasty in Chinese historiography. It existed from 2070-1600 BCE, and was established by a legendary figure known as Yu the Great. The dynasty is credited with establishing centralized governance, agriculture and irrigation, and generally shifting China from a prehistoric to a historical period.
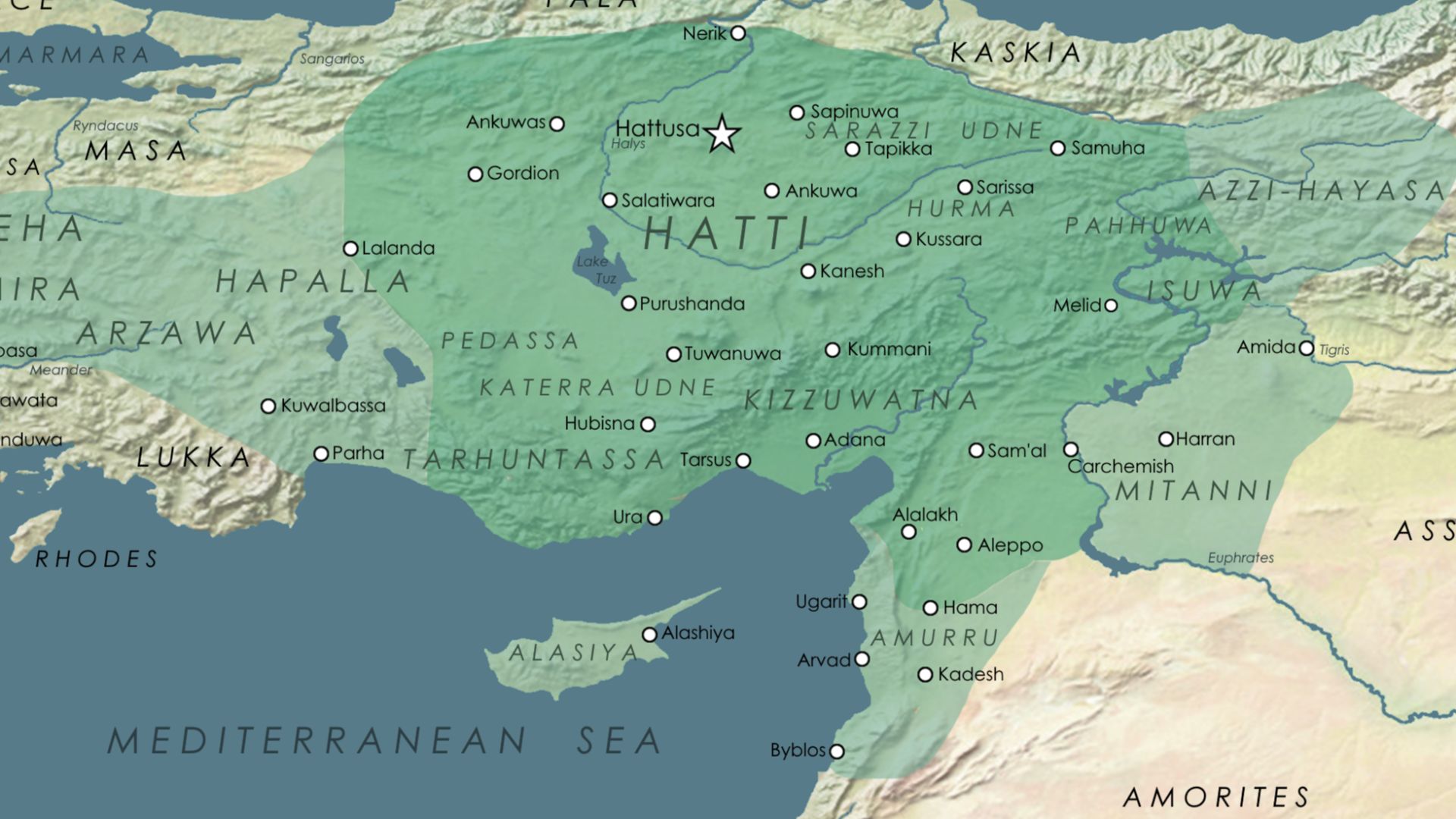
14. The Hittites
The Hittite Empire existed from 1650 to 1180 BCE in modern-day Turkey. They’re considered one of the first Bronze Age civilizations in West Asia, and their influence spread to several kingdoms, including Kussara, Kanesh, and Hattusa.
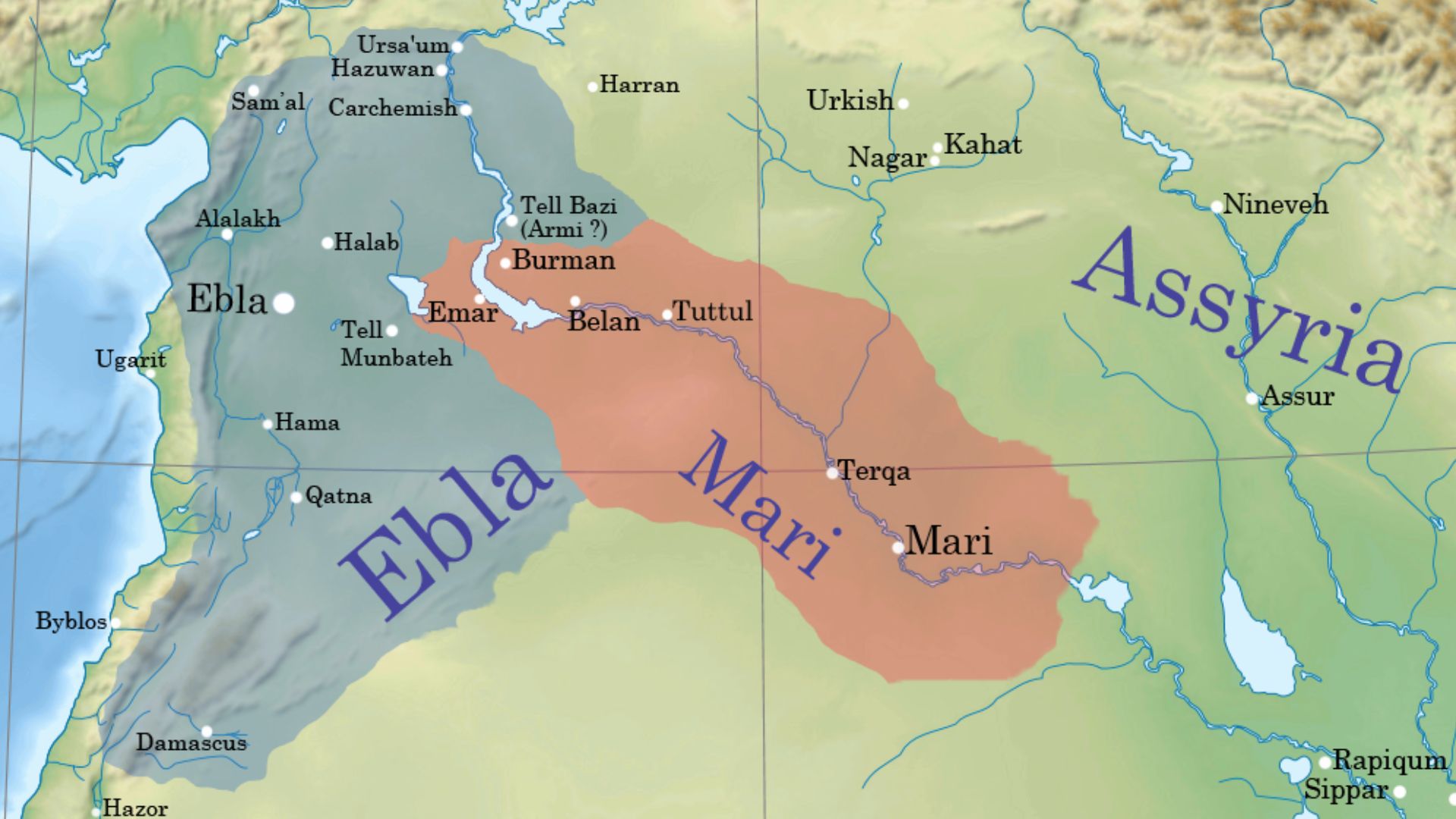
15. The Kingdom Of Ebla
Existing from 3500 BCE to the 800s CE, the Ebla empire is one of the earliest and longest-lasting kingdoms in modern-day Syria. Ebla is known for a vast trading empire, and the Levant region of this kingdom was parallel to Egypt and Mesopotamia’s importance throughout the Bronze Age.
16. Ancient Carthage
The Carthaginian Empire existed from 814 BCE to 146 BCE. Settling originally in modern-day Tunisia, Carthage’s influence spread over the central-western Mediterranean Sea. The city of Carthage is considered one of the largest the world had seen to date, and was rich in money and in fertile land.
17. Babylonian Empire
The Babylonian Empire was established in 1890 BCE and lasted until 539 BCE. It was part of the south-central area of Mesopotamia, and was known to speak Akkadian. Babylonia is well known for Hammurabi’s Code, one of the earliest legal codes in history, as well as advancements in astronomy and geometry.
18. Assyrian Empire
The Assyrian Empire existed as part of ancient Mesopotamia from 2500 BCE to 240 CE. It originally existed as a city-state for the first few centuries of its life, before expanding into a full-fledged empire in the 14th century BCE. It was well-known for advanced military tactics and weaponry, as well as a well-developed postal system.
 Russell & Struthers Engravers, New York on Wikimedia
Russell & Struthers Engravers, New York on Wikimedia
19. Yayoi Period
Not technically a civilization, but an important transitional era of the Japanese archipelago. This particular period lasted from 300 BCE to 300 CE, and is noted as the switch from a hunter-gatherer economy to a productive economy.
20. Aksumite Empire
This empire was a powerful trading kingdom that lasted from the 1st century to the 10th century CE in modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. It’s considered one of the four great powers during the third century alongside Persia, Rome, and China. This empire was well-known for its role in the Indian Ocean trade, architectural achievements such as the Obelisks of Aksum, and for minting its own coins.
KEEP ON READING

The Fertile Crescent: 20 Ancient Civilizations That Started Society As…
Thank You For Your Service. Human society had to start…
By Breanna Schnurr Sep 11, 2025
10 Polar Explorers Who Made Mistakes & 10 Who Made…
Explorers Who Redefined The Map. Antarctic explorer Apsley Cherry-Garrard once…
By Ashley Bast Sep 10, 2025
20 Constellations With Fascinating Ancient Histories
Stories Written In The Sky Long Before We Arrived. Every…
By Cameron Dick Sep 10, 2025
20 Women Forgotten by History
Alice Ball Helped Cure Leprosy. Women have often been sidelined…
By Rob Shapiro Sep 10, 2025
20 Foods That Changed History
They Don't Just Shape Our Diets. Food is something humans…
By Emilie Richardson-Dupuis Sep 9, 2025
20 Terrifying Cursed Objects Throughout History
Don’t Look in the Mirror. Cursed objects with a history…
By Farva Ivkovic Sep 9, 2025